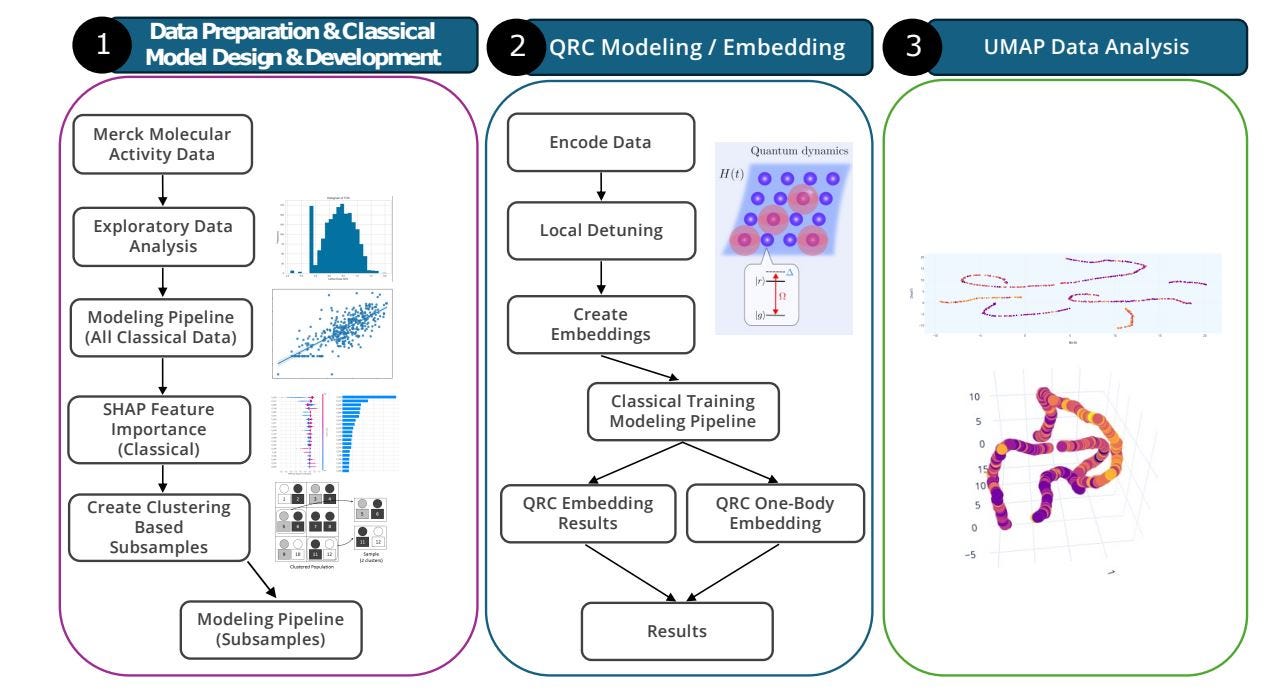
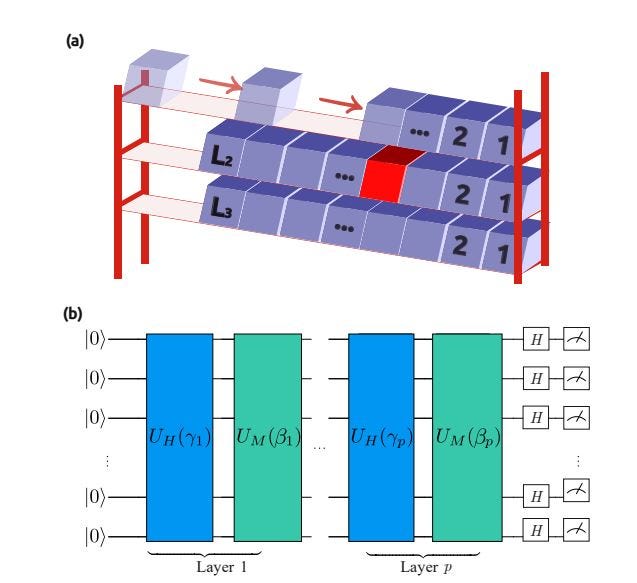
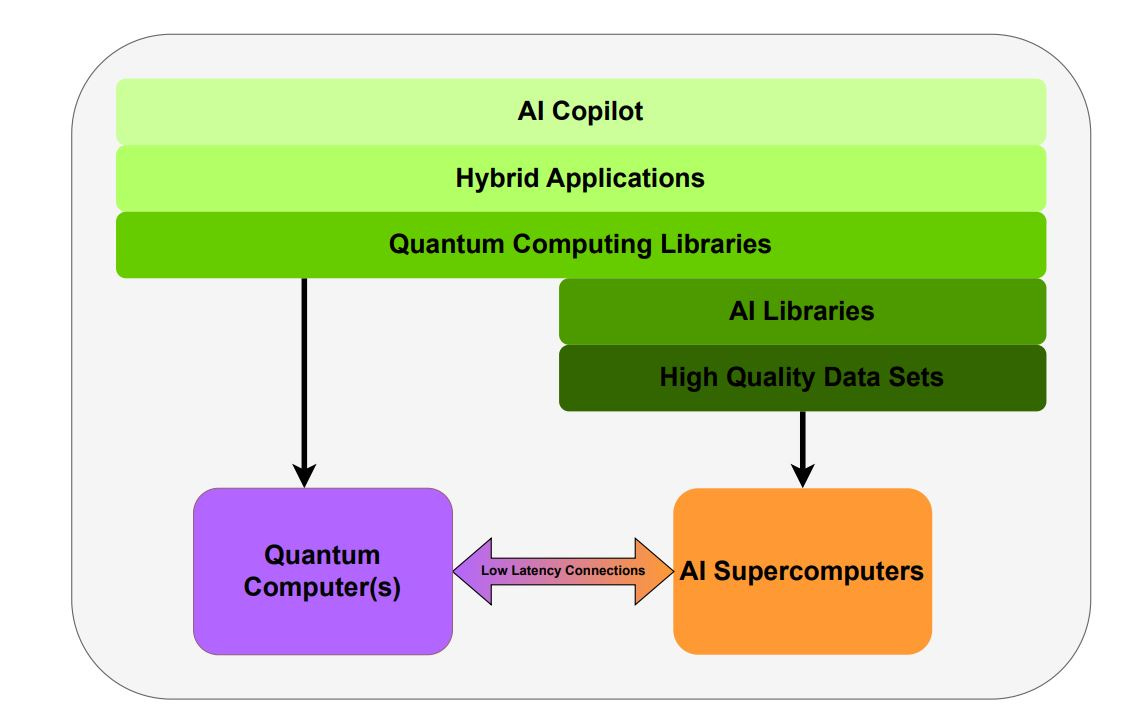
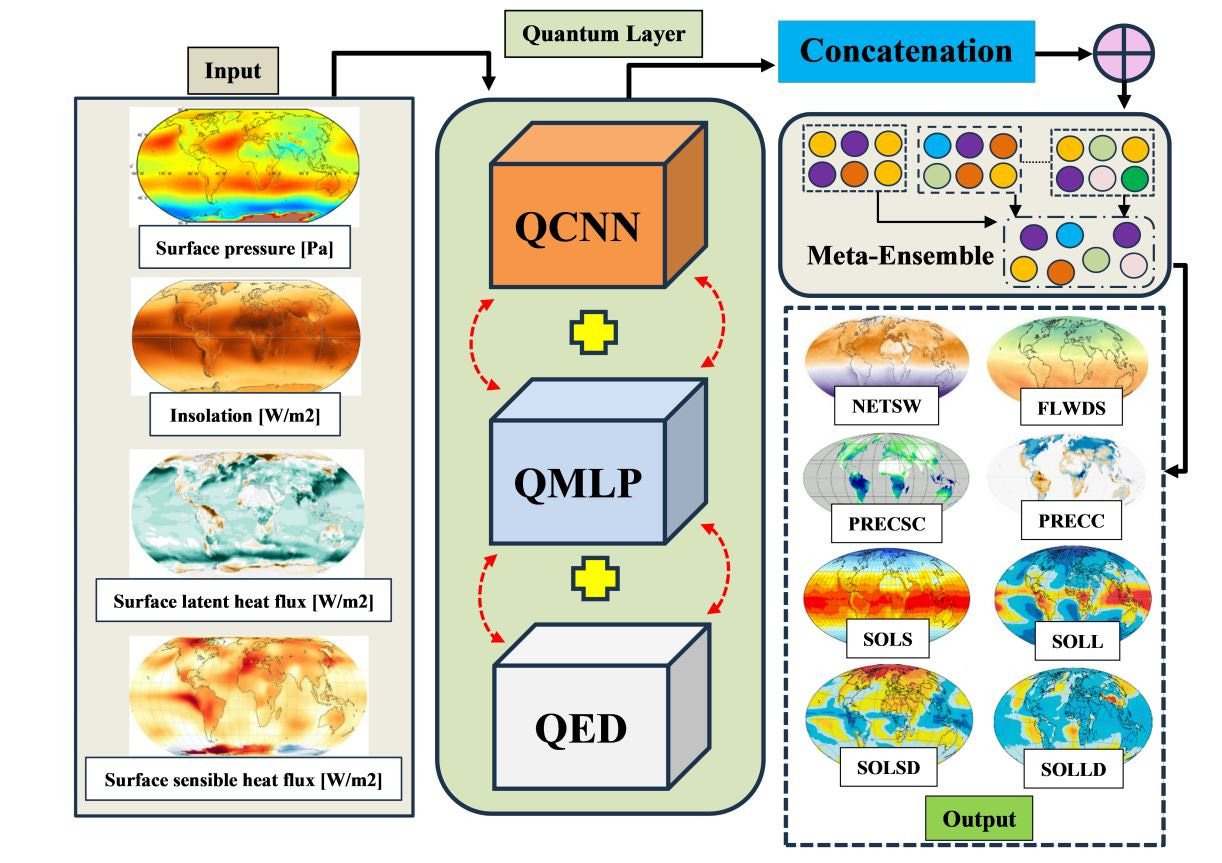
Why Willow Google Quantum Chip Will Change the Computing Landscape in the Next Years
A real quantum leap in the future
In the world of quantum computing, 2024 marks a pivotal year with Google's recent announcement of its groundbreaking quantum chip, Willow.
A step forward in the quantum realm, Willow brings a new level of promise, potential, and concern to the forefront of technology. As quantum computing inches closer to real-world applications, Willow’s advancements signal transformative shifts across industries, from cryptography to artificial intelligence, and possibly redefine how we understand computation itself.
Crossing the Quantum Error Correction Threshold
One of the most critical hurdles in quantum computing has been error rates. Quantum systems, traditionally plagued by inaccuracies, grow more error-prone as their complexity increases. Willow, however, represents a quantum leap in error correction. With improved design and fabrication, Google’s chip has surpassed a vital milestone—a critical error correction threshold—where the system’s accuracy improves as it scales to larger numbers of qubits.
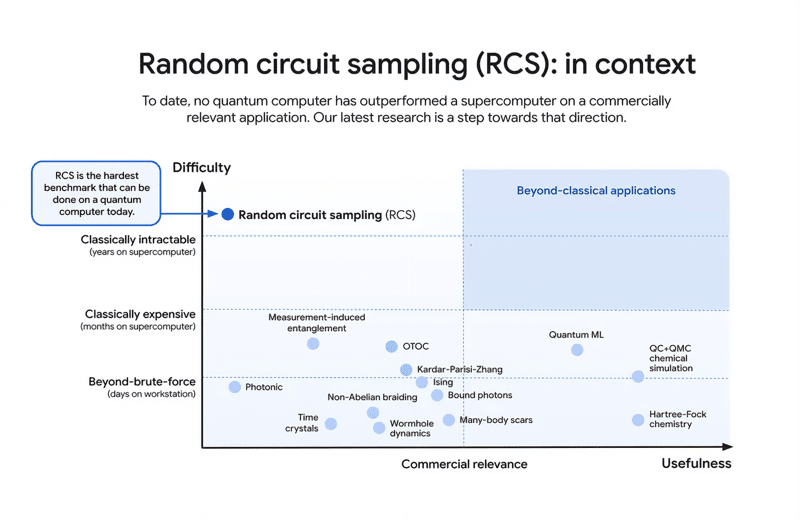
This breakthrough is monumental. It means that, for the first time, adding more qubits to a quantum system does not exacerbate error rates but instead helps mitigate them. The chip has shown an ability to complete computations previously thought impossible: tasks that would take classical supercomputers septillion years (10^25) to accomplish can now be completed in five minutes. This achievement demonstrates that quantum systems can now operate with a level of reliability that hints at broader, real-world applications in the near future.
The Daunting Road to Fault Tolerance
While Willow’s error rate improvement is impressive, true fault tolerance remains an elusive goal. Google’s quantum team needs to improve error rates by several orders of magnitude—from 10^-3 to 10^-6—a significant challenge. Despite these technical hurdles, the progress made from 53 qubits to 105 qubits over the past five years highlights the accelerating pace of innovation. This scaling suggests that quantum computing could achieve commercially relevant applications in fields like materials science, optimization problems, and cryptography sooner than expected.
Competition in the Quantum Computing Space
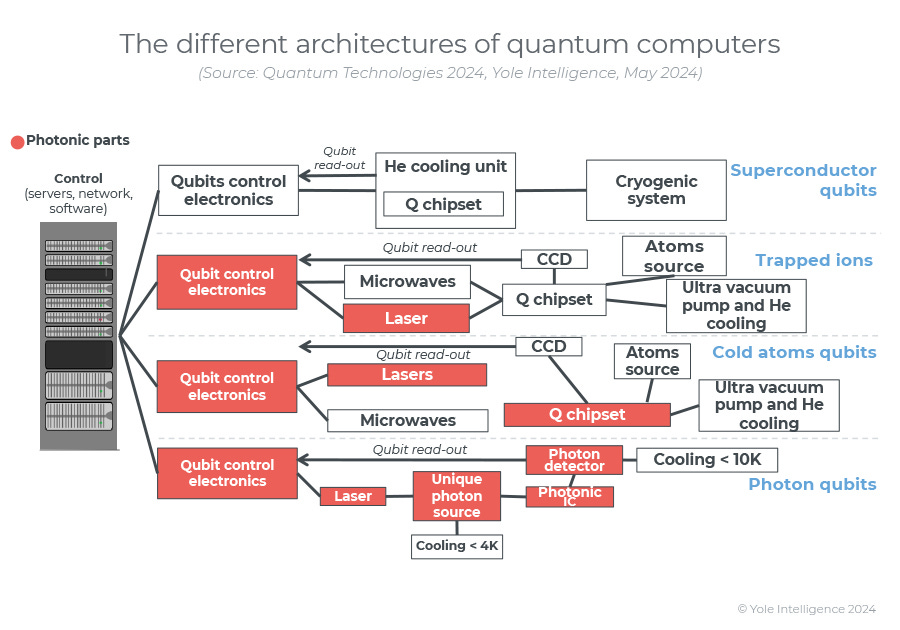
Google’s Willow is not alone in this race. Companies like IBM and startups such as IONQ have also made strides in quantum computing. IBM’s Eagle processor, with 127 qubits, set a benchmark in 2021, and their ongoing efforts focus on modular quantum processors that could scale up to thousands of qubits. Similarly, InQ’s approach leverages trapped-ion technology, offering a different path to reliable quantum computation.
A common theme across competitors is the shift from massive, physics-intensive setups to wafer-based quantum chips, signaling a move toward more compact and scalable designs. This evolution is crucial for quantum systems to transition from experimental physics laboratories to commercial data centers.
Implications for Cryptography and Blockchain
Willow’s potential capabilities have reignited debates in the blockchain and cryptography communities. Modern cryptographic protocols, such as those underpinning Bitcoin and Ethereum, rely on the difficulty of certain mathematical problems—problems that quantum computers could potentially solve in seconds. This raises significant concerns about transaction authorization, proof-of-work mining, and the security of dormant Bitcoin wallets.
While quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms exist and Ethereum has committed to adopting quantum-secure protocols, Bitcoin faces a unique challenge. Maintaining Bitcoin’s ethos of ossification—its resistance to change—while addressing quantum risks is a delicate balancing act. Longtime Bitcoin developers, including Jameson Lopp, are actively exploring solutions to ensure the network’s integrity remains intact before quantum threats become tangible.
Potential Applications of Quantum Computing
Beyond cryptography, the implications of quantum computing are vast:
Drug Discovery and Material Science: Quantum computers could simulate molecular interactions at an unprecedented level, accelerating the development of new drugs and materials.
Optimization Problems: Industries like logistics, finance, and energy could leverage quantum algorithms to solve optimization problems that are infeasible for classical systems.
Artificial Intelligence: Enhanced machine learning models could emerge from quantum computing’s ability to process complex datasets and algorithms more efficiently.
Climate Modeling: Quantum systems may enable precise modeling of climate systems, providing insights into mitigation strategies and renewable energy optimization.
From Physics Labs to Commercial Data Centers
One of the most exciting aspects of Willow and its contemporaries is the transition from massive setups requiring highly controlled environments to more scalable, chip-based architectures. This shift could pave the way for quantum computing to be integrated into existing data center infrastructures, democratizing access and expanding its applications.
A Paradigm Shift in Computing
Willow’s advancements herald a new era in computing, with profound implications for technology and society. While challenges remain—particularly in achieving true fault tolerance and addressing security concerns—the progress made so far suggests that quantum computing is on the brink of practical utility. As companies like Google, IBM, and others continue to push the boundaries, the potential for a quantum-powered future becomes increasingly tangible. Willow may very well be the catalyst that redefines our computational landscape, forever changing how we solve problems, secure data, and advance technology.